Identification types and nutritional composition of traditional pig feed in rural areas of Timor Island and its influence on production efficiency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46549/jipvet.v15i4.547Keywords:
Identification, Local feed, Nutritional composition, Pig farming, Production efficiencyAbstract
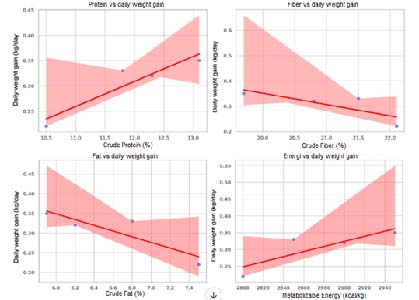
The use of traditional feed depends on the location of pig production. Information regarding traditional ration variations and nutritional content is not yet available, especially in rural areas of Timor Island. This research aims to identify the types and nutritional composition of traditional feeds used in rural pig rearing and to analyze their effects on production efficiency. The study was conducted in four villages in Taebenu District, Kupang Regency. This research used a descriptive observational design with a cross-sectional approach. Data collection was carried out to provide an overview of the types of traditional feed used, their nutritional composition, and their relationship to production efficiency. The data obtained were analyzed descriptively to describe the distribution of feed types and their nutritional composition; Pearson correlation tests and linear regression analyses were used to determine the relationships and their influence on production efficiency. The results of the research show that the composition of traditional feed across the four sampling locations is generally not much different and is highly diverse, which affects the diversity of its nutritional value. In this study, there was a positive correlation between nutrition and body weight gain and feed conversion. At the same time, regression analysis showed that crude protein and metabolic energy were the main factors that increased production efficiency. Based on the results of this research, it can be concluded that variations in local feed types result in differences in nutritional composition. The results of correlation analysis show that feed composition has a significant influence on the growth and production efficiency of pigs, crude protein and energy metabolism have a positive relationship with body weight gain and negative with feed conversion, while crude fiber has the opposite effect, regression analysis shows that crude protein and metabolic energy are the main factors that increase production efficiency, while crude fiber interferes with livestock performance.
Downloads
References
Asben A, Taib G, Rahmawati Y. 2019. Studi karakteristik selai kolang kaling markisa dengan penambahan pewarna angkak. Journal of Applied Agricultural Science and Technology. 3(1); 1–14. https://doi.org/10.32530/jaast.v3i1.61.
Atma Y. 2015. Studi penggunaan angkak sebagai pewarna alami dalam pengolahan sosis daging sapi. Jurnal Teknologi. 7(2); 76–85.
Hutasoit DP. 2020. Pengaruh sanitasi makanan dan kontaminasi bakteri Escherichia coli terhadap penyakit diare. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Sandi Husada. 12(2); 779–786. https://doi.org/10.35816/jiskh.v12i2.399.
Indriati N, Fairdiana A. 2012. Pemanfaatan angkak sebagai pewarna alami pada terasi udang. Jurnal Pascapanen dan Bioteknologi Kelautan dan Perikanan. 7(1); 11–20. https://doi.org/10.15578/jpbkp.v7i1.65
Iqbal M, Rochmah AN. 2023. Keamanan pangan: higiene dan sanitasi usaha jasa boga. Penerbit Salemba.
Malelak GE. 2015. Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Schleichera oleosa liquid smoke on lipid content, lipid oxidation and residual nitrite in se’i (Rotenese smoked beef). ISTAP; 683–687.
Nguyen T, Karl M, Santini A. 2017. Red yeast rice. Foods. 6(3); 1–4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6030019
Noviana N, Ruhban A. 2020. Identifikasi kandungan bakteri Escherichia coli dan Salmonella pada burger yang dijual pedagang kaki lima di Kota Makassar. Sulolipu: Media Komunikasi Sivitas Akademika dan Masyarakat. 19(2); 259–265. https://doi.org/10.32382/sulolipu.v19i2.1348
Ramadhan AF, Radiati LE, Thohari I. 2005. Tingkat penggunaan ekstrak angkak (Monascus purpureus) sebagai curing alternatif dengan metode curing basah terhadap kualitas kornet daging sapi. Jurnal Universitas Brawijaya; 1–7.
Resti R. 2024. Formulasi sediaan lip cream menggunakan ekstrak daun jati (Tectona grandis Lf) sebagai pewarna alami [Disertasi Doktoral]. Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Barat, Padang.
Risando YK. 2023. Pengaruh liofilisasi bakteri Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 dengan serum kuda sebagai lioprotektan yang disimpan selama dua bulan pada suhu ruang terhadap viabilitas, morfologi dan biokimia [Disertasi Doktoral]. Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta.
Sabtu B, Suryatni NPF. 2015. Kualitas kimia daging se’i yang diberi ekstrak angkak dan lama penyimpanan berbeda. Jurnal Nukleus Peternakan. 2(1); 7–14.
Sari WK, Astutiningsih C, Suharsanti R, Wulan AAH. 2019. Kajian manajemen produksi pewarna alami angkak powder yang berpotensi sebagai antioksidan dan antibakteri. Jurnal Farmasi & Sains Indonesia. 2(1); 99–105.
Shakil MH, Trisha AT, Rahman M, Talukdar S, Kobun R, Huda N, Zzaman W. 2022. Nitrites in cured meats, health risk issues, alternatives to nitrites: A review. Foods. 11(21); 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213355
Sunayardi Z, Balia RL, Suryaningsih L. 2021. Karakteristik mutu sei sapi yang diolah secara tradisional terhadap berbagai kombinasi waktu dan suhu pengasapan. Jurnal Ilmu Ternak Universitas Padjadjaran. 21(1); 58–65. https://doi.org/10.24198/jit.v21i1.34544
Ummami R, Risa, Ramandani D, Airin CM, Husni A, Astuti P. 2022. Uji kualitas dan uji cemaran daging babi pada daging sapi di beberapa pasar tradisional di Yogyakarta. Jurnal Ilmu Peternakan dan Veteriner Tropis. 12(2); 151. https://doi.org/10.46549/jipvet.v12i2.277
Zhao CJ, Schieber A, Gänzle MG. 2016. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations – a review. Food Research International. 89; 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.08.042
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fredeicus D. Samba, Ni P. F. Suryatni, Juliana M. Nepa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
In submitting the manuscript to the journal, the authors certify that:
- They are authorized by their co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- The work described has not been formally published before, except in the form of an abstract or as part of a published lecture, review, thesis, or overlay journal. Please also carefully read Jurnal Ilmu Peternakan dan Veteriner Tropis (Journal of Tropical Animal and Veterinary Science) Posting Your Article Policy at https://journal.fapetunipa.ac.id/index.php/JIPVET/publicationethics
- That it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere,
- That its publication has been approved by all the author(s) and by the responsible authorities “tacitly or explicitly“ of the institutes where the work has been carried out.
- They secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- They agree to the following license and copyright agreement.
Copyright
Authors who publish with Jurnal Ilmu Peternakan dan Veteriner Tropis (Journal of Tropical Animal and Veterinary Science) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.























.png)
